04 Dec 2025
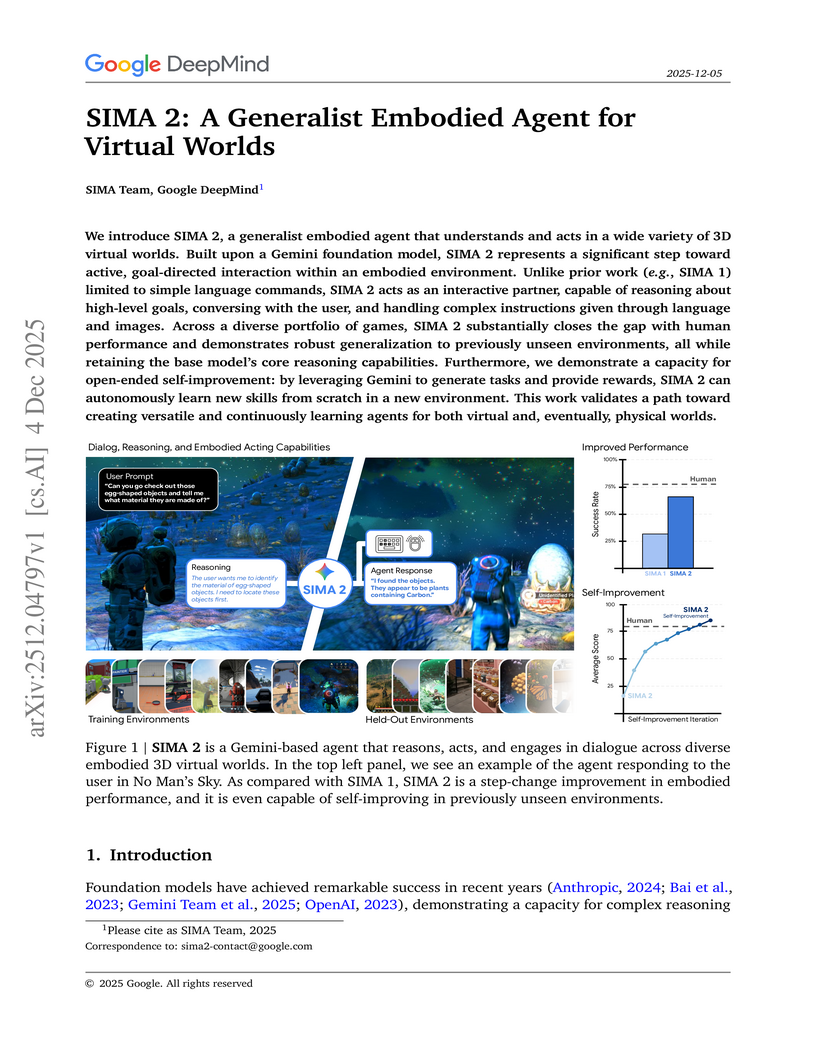
Google DeepMind developed SIMA 2, a generalist embodied agent powered by a Gemini Flash-Lite model, capable of understanding and acting in diverse 3D virtual worlds. It substantially doubles the task success rate of its predecessor SIMA 1, generalizes to unseen commercial games and photorealistic environments, and demonstrates autonomous skill acquisition through a Gemini-based self-improvement mechanism.
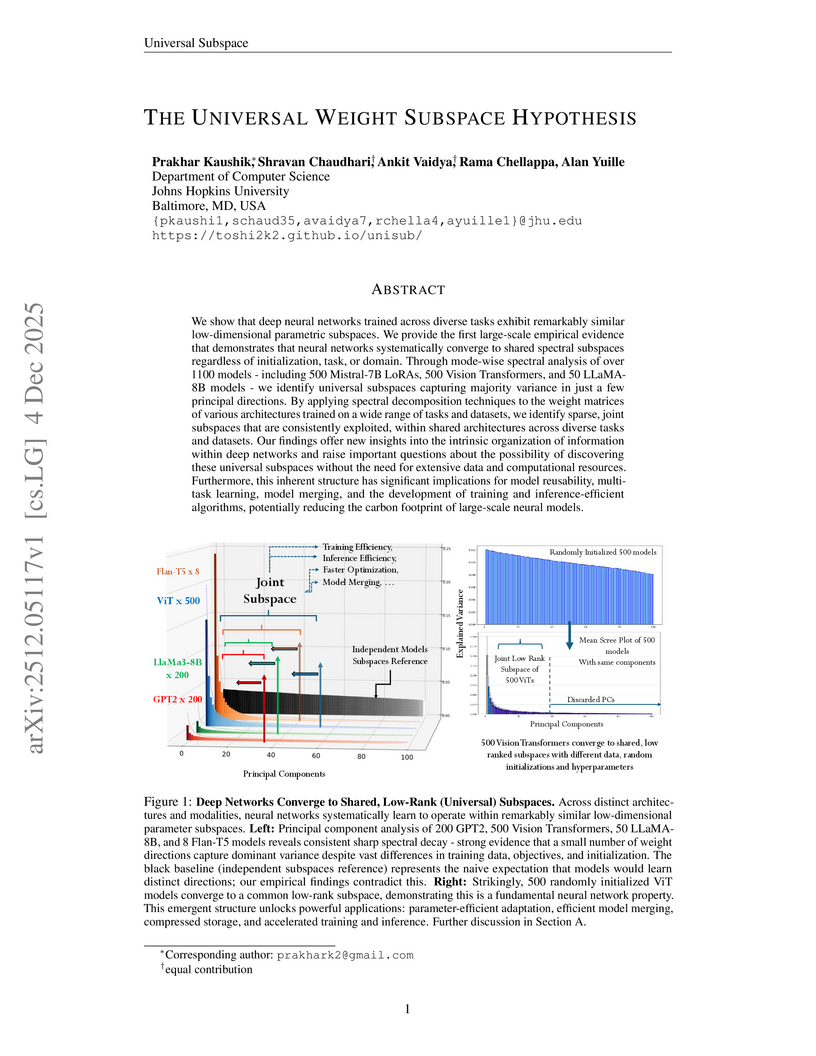
Researchers at Johns Hopkins University empirically validated the Universal Weight Subspace Hypothesis, showing that deep neural networks consistently converge to shared, low-dimensional parametric subspaces within their weight matrices, irrespective of training conditions. This underlying structure allows for substantial memory efficiency (e.g., over 100x reduction), enables parameter-efficient adaptation to new tasks with competitive performance, and outperforms model merging baselines.
02 Dec 2025
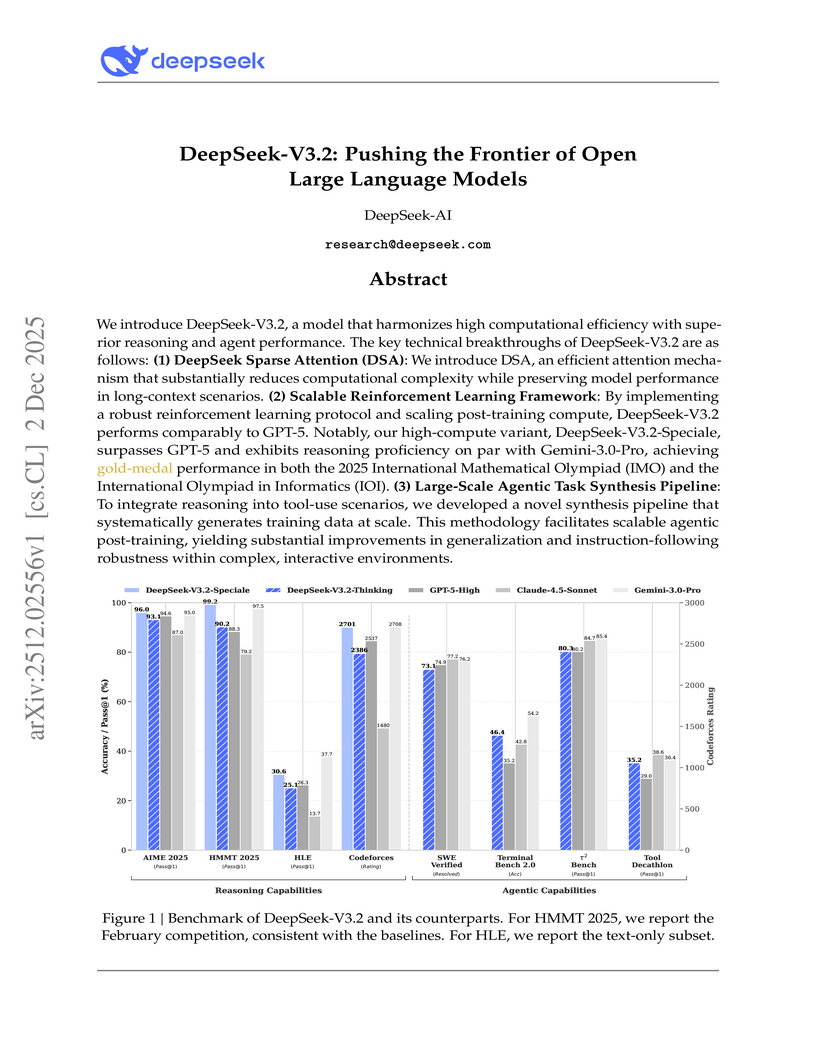
DeepSeek-AI developed DeepSeek-V3.2, an open large language model featuring DeepSeek Sparse Attention for improved efficiency and a scalable reinforcement learning framework, aiming to bridge the performance gap with proprietary models. The model, particularly its 'Speciale' variant, achieves gold-medal performance in elite competitions like the International Mathematical Olympiad and International Olympiad in Informatics, while also advancing agentic capabilities on various benchmarks.
04 Dec 2025
Researchers from Google, NYU, ETH Zurich, and Stanford present a theoretical framework to formalize how large language models perform complex, iterative reasoning. The framework characterizes reasoning "oracles" and algorithms, proving that branching and genetic algorithms can achieve optimal success probabilities for models where oracle accuracy can decay with context size, and explains phenomena like "overthinking."
The Nex-AGI Team developed a unified ecosystem, Nex, for constructing large-scale, diverse, and realistically grounded interactive environments to train autonomous AI agents. Their Nex-N1 models, trained using this infrastructure, demonstrate competitive to superior performance on complex agentic tasks, including coding and deep research, across various benchmarks and real-world evaluations.
03 Dec 2025
Researchers from Zhejiang University and ByteDance introduced CodeVision, a "code-as-tool" framework that equips Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to programmatically interact with images. The approach significantly improves MLLM robustness by correcting common image corruptions and enables state-of-the-art multi-tool reasoning through emergent tool use and error recovery.
02 Dec 2025
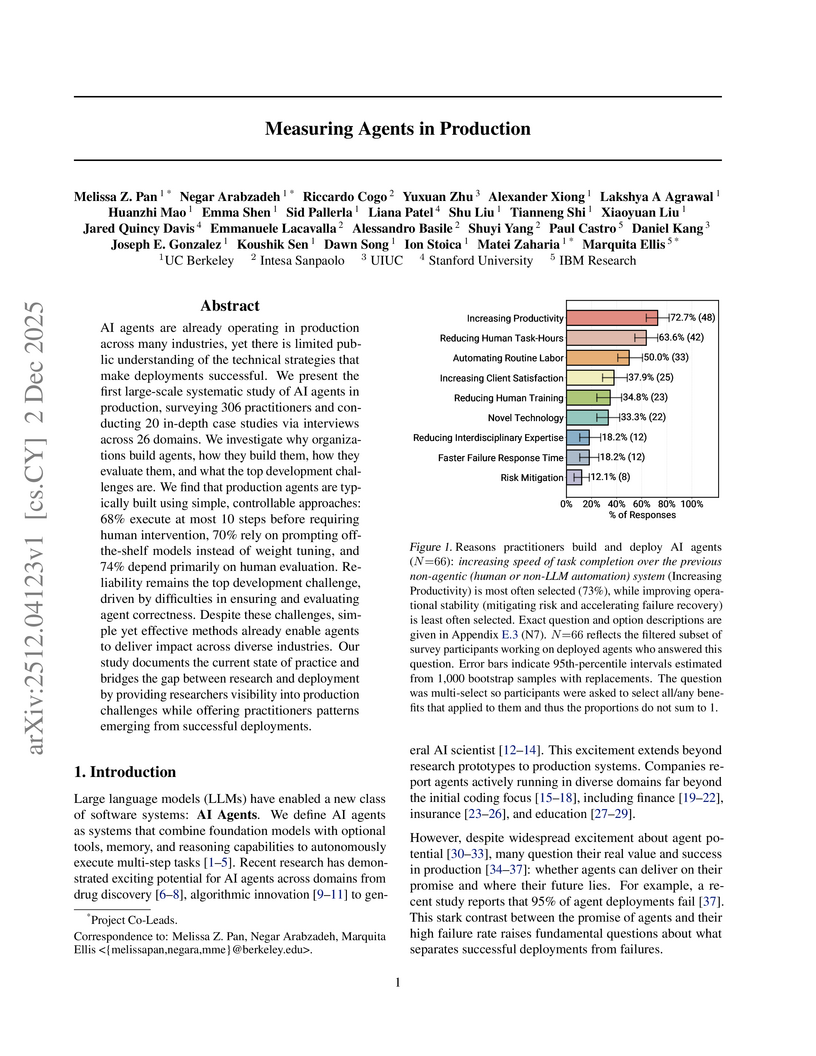
An empirical study surveyed 306 AI agent practitioners and conducted 20 in-depth case studies to analyze the technical strategies, architectural patterns, and challenges of successfully deployed AI agents. The research reveals how real-world production agents prioritize reliability and controlled autonomy to achieve productivity gains across diverse industries.
Researchers from Alibaba Group and USTC developed Live Avatar, an algorithm-system co-designed framework for real-time, high-fidelity, and infinite-length audio-driven avatar generation using a 14-billion-parameter diffusion model. The system achieves 20.88 FPS and demonstrates visual consistency for over 10,000 seconds, significantly advancing practical applications.
The Qwen Team at Alibaba Inc. developed a theoretical formulation that justifies token-level optimization for sequence-level rewards in Large Language Model (LLM) reinforcement learning, identifying training–inference discrepancy and policy staleness as key instability factors. Their work also provides empirically validated strategies, including Routing Replay and clipping, to achieve stable and high-performing RL training for Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) LLMs.
04 Dec 2025
Researchers from UC Berkeley and ByteDance Seed developed Natural Language Actor-Critic (NLAC), an off-policy reinforcement learning algorithm that trains LLM agents using a generative natural language critic to provide rich, explanatory feedback. NLAC demonstrated superior performance and enhanced sample efficiency on multi-turn dialogue and tool-use tasks compared to existing RL methods and strong prompting baselines.
Huawei Inc. researchers introduce EMMA, a unified multimodal architecture for efficient understanding, generation, and editing. EMMA achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming larger unified models like BAGEL-7B by 5.8% on MMVet and reaching 0.91 on GenEval, while requiring significantly fewer visual tokens, such as 1/5 for image editing.
Semantic Soft Bootstrapping (SSB), an RL-free self-distillation framework developed at the University of Maryland, enhances large language model reasoning by having the model act as both teacher and student. It boosted pass@1 accuracy on the MATH500 benchmark by 10.6% and on AIME2024 by 10% over a GRPO baseline, while utilizing a smaller dataset and maintaining concise response lengths.
The `GenMimic` framework enables humanoid robots to execute actions from noisy, AI-generated videos in a zero-shot manner by combining 4D human reconstruction and retargeting with a robust reinforcement learning policy. This approach facilitates successful physical reproduction on a Unitree G1 robot and demonstrates improved performance on a newly introduced benchmark dataset of synthetic motions.
Researchers at KAIST AI introduce Deep Forcing, a training-free method for long video generation that extends pre-trained autoregressive diffusion models to produce minute-long videos. The approach achieves state-of-the-art performance, delivering superior temporal consistency, aesthetic quality, and dynamic motion compared to training-based methods, without additional fine-tuning.
Reward Forcing introduces EMA-Sink and Rewarded Distribution Matching Distillation (Re-DMD) to enable efficient, real-time streaming video generation. This framework achieves an overall VBench score of 84.13 and a generation speed of 23.1 FPS, while significantly enhancing motion dynamics and maintaining long-horizon consistency.
A theoretical framework unifies continuous and discrete diffusion models, presenting parallel discrete-time and continuous-time formulations using SDEs and CTMCs. It clarifies how forward corruption processes dictate reverse dynamics and training objectives, deriving common loss functions like Denoising Score Matching and Masked Language Modeling from a single variational inference principle.
04 Dec 2025
Researchers developed SEAL, a self-evolving agentic learning framework for conversational question answering over knowledge graphs that employs a two-stage parsing mechanism to generate structurally accurate logical forms from natural language. It reached an overall accuracy of 66.83% on the SPICE benchmark, significantly surpassing unsupervised baselines and showing strong performance on complex multi-hop, quantitative, and comparative reasoning.
Instruction-based image editing has emerged as a prominent research area, which, benefiting from image generation foundation models, have achieved high aesthetic quality, making instruction-following capability the primary challenge. Existing approaches improve instruction adherence via supervised or reinforcement learning, yet single-turn success rates remain limited due to inherent stochasticity and a lack of deliberation. In this work, we propose a deliberative editing framework to 'think' while they edit, which simulates the human cognitive loop by iteratively executing a Think-while-Edit cycle: Critiquing results and Refining instructions , followed by Repeating the generation until satisfactory. Specifically, we train a single MLLM, EditThinker, to act as the reasoning engine of this framework, which jointly produce the critique score, reasoning process, and refined instructions. We employ reinforcement learning to align the EditThinker's thinking with its editing, thereby generating more targeted instruction improvements. Extensive experiments on four benchmarks demonstrate that our approach significantly improves the instruction-following capability of any image editing model by a large margin. We will release our data construction framework, datasets, and models to benefit the community.
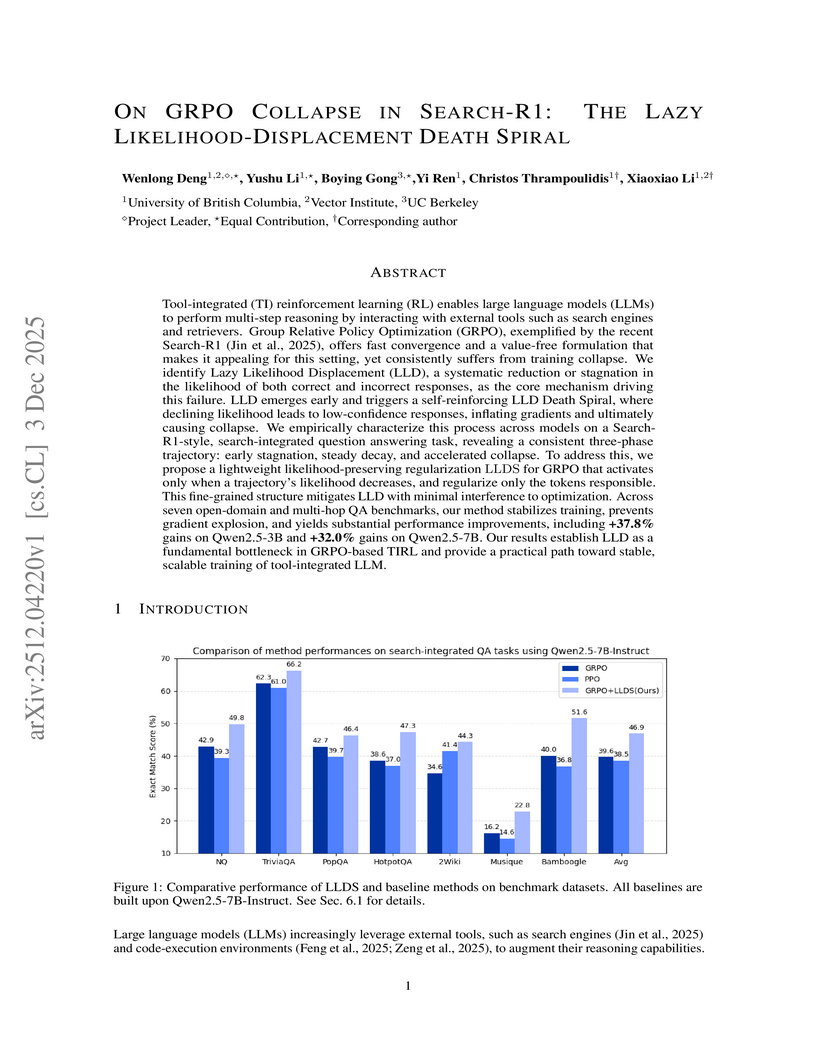
This work from the University of British Columbia, Vector Institute, and UC Berkeley diagnoses "Lazy Likelihood Displacement (LLD)" as the root cause of training collapse in Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) for tool-integrated Large Language Models. It introduces Likelihood-preserving Regularization (LLDS) to stabilize training, achieving up to a +37.8% relative gain in performance on multi-hop question answering benchmarks and preventing catastrophic failures.
Researchers at Shanghai AI Lab and collaborating institutions introduced ARM-Thinker, a framework that integrates agentic tool use and visual reasoning into multimodal generative reward models. This approach allows models to actively verify information, leading to improved reliability, interpretability, and an average performance gain of 16.2% on reward modeling benchmarks.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.